GitOps with Argo CD
Cosmonic Control integrates seamlessly with continuous delivery systems such as Argo CD to enable GitOps patterns, in which Git repositories serve as the source of truth for application state. You can specify Kubernetes manifests to Argo CD in various ways, including as Helm charts and directories of YAML manifests.
In this section, you'll learn...
- How to deploy and manage Cosmonic Control with Argo CD
- How to deploy and manage Wasm components with Argo CD
The manifest and values file used in this guide are available in the control-demos repository on GitHub.
Requirements
kubectl- Helm v3.8.0+
- GitHub account
- Free trial key for Cosmonic Control
Install local Kubernetes environment
Install kind with the following kind-config.yaml configuration:
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
# One control plane node and three "workers."
nodes:
- role: control-plane
extraPortMappings:
- containerPort: 30950
hostPort: 80
protocol: TCPThis will help enable simple local ingress with Envoy.
Start the cluster:
kind create cluster --config=kind-config.yamlFork the demo repository
Navigate to the control-demos repository in GitHub and create a fork of the repo. (Throughout these instructions, we'll assume that you use the name control-demos for your fork—everything will still work if you change the name, but remember to adjust the commands accordingly.)

You can either clone the repo locally or work entirely in the browser. The only significant difference is that you'll need to copy and paste a few Argo CD Application CRD manifests if you work in the browser.
If you decide to clone the repo, navigate to the argo-cd subdirectory:
git clone https://github.com/<your-github-namespace>/control-demos.gitcd control-demos/integrations/argo-cdDeploy Argo CD
If you do not have Argo CD running on your cluster already, you can deploy a simple example installation of Argo CD using the community-maintained Helm chart:
helm install argocd oci://ghcr.io/argoproj/argo-helm/argo-cd --set-string configs.params."server\.disable\.auth"=true --version 8.1.3 --create-namespace -n argocdThis is a simple example deployment of Argo CD for demonstration purposes, running without authentication.
Port-forward the Argo CD server in order to access the Argo CD dashboard. (Note: We're using our local port 3000 for the Argo CD dashboard in order to leave 8080 for the Cosmonic Control Console UI.)
kubectl port-forward service/argo-cd-argocd-server -n argocd 3000:443You should see the Argo CD dashboard at localhost:3000. At the moment, there won't be any running Argo CD Applications, the high-level abstraction used by Argo CD for managed deployments.
Deploy Cosmonic Control
You'll need a trial license key to follow these instructions. Sign up for Cosmonic Control's free trial to get a key.
Use the following Argo Application CRD manifest in a file called control-proj.yaml to define your deployment of Cosmonic Control. (Remember to include your trial license key.)
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: cosmonic-control
namespace: argocd
annotations:
# ArgoCD will apply this manifest first.
argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave: '1'
spec:
project: default
source:
chart: cosmonic-control
repoURL: ghcr.io/cosmonic
targetRevision: 0.3.0
helm:
valuesObject:
cosmonicLicenseKey: '<insert license here>'
envoy:
service:
type: NodePort
httpNodePort: 30950
destination:
name: 'in-cluster'
namespace: cosmonic-system
syncPolicy:
automated: {}
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
retry:
limit: -1
backoff:
duration: 30s
factor: 2
maxDuration: 5mApply the manifest with kubectl:
kubectl apply -f control-proj.yamlNow deploy a HostGroup using an Argo Application CRD manifest called hostgroup-proj.yaml:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: hostgroup
namespace: argocd
annotations:
# ArgoCD will apply this manifest first.
argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave: '1'
spec:
project: default
source:
chart: cosmonic-control-hostgroup
repoURL: ghcr.io/cosmonic
targetRevision: 0.3.0
destination:
name: 'in-cluster'
namespace: cosmonic-system
syncPolicy:
automated: {}
retry:
limit: -1
backoff:
duration: 30s
factor: 2
maxDuration: 5mApply the manifest:
kubectl apply -f hostgroup-proj.yamlThe Applications will appear on the Argo CD dashboard. It may take a moment for the Applications to finish syncing.
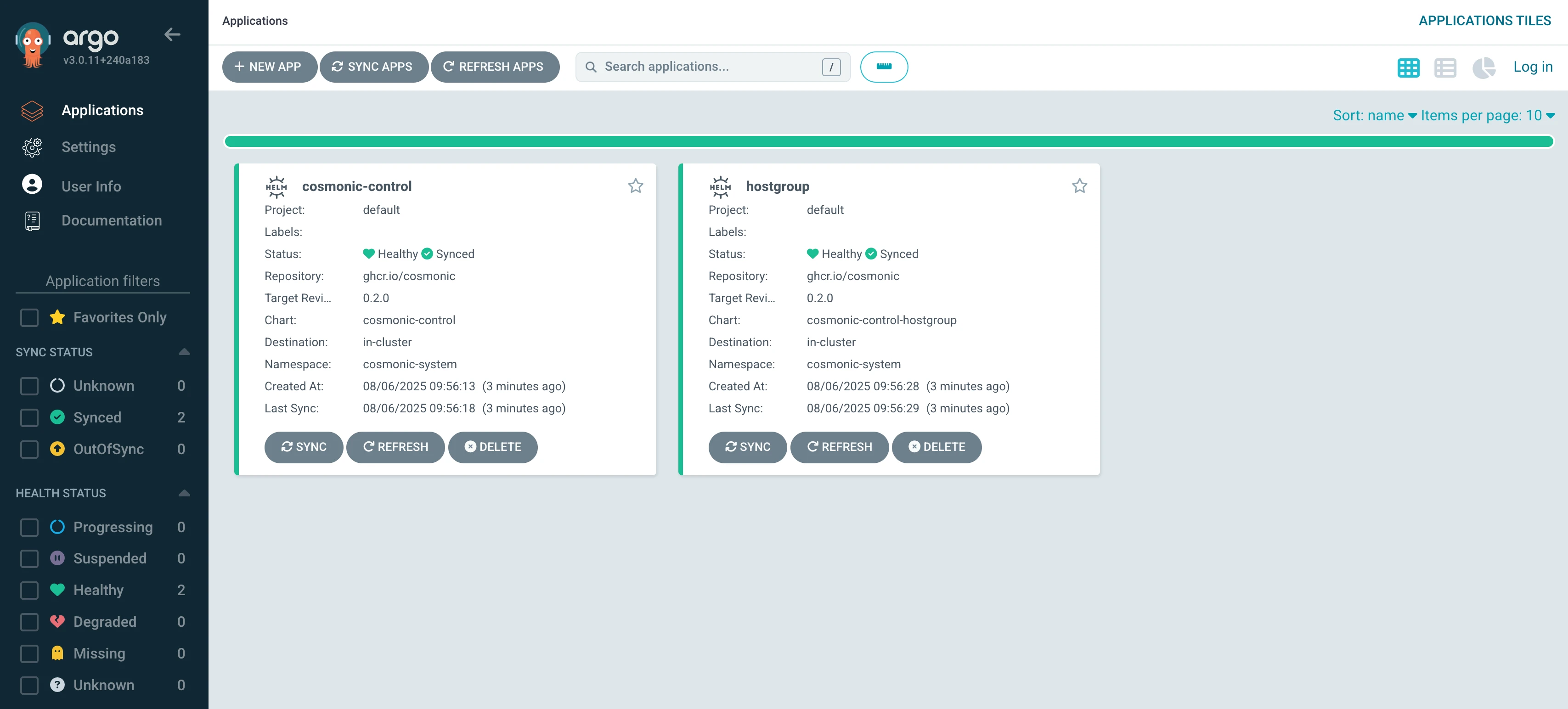
Once the Applications are synced and healthy, you can port-forward to access the Cosmonic Control Console UI at localhost:8080:
kubectl -n cosmonic-system port-forward svc/console 8080:8080Trigger Wasm workload sync via GitHub release
Now let's try a more in-depth GitOps workflow to trigger a Wasm workload sync with a GitHub release.
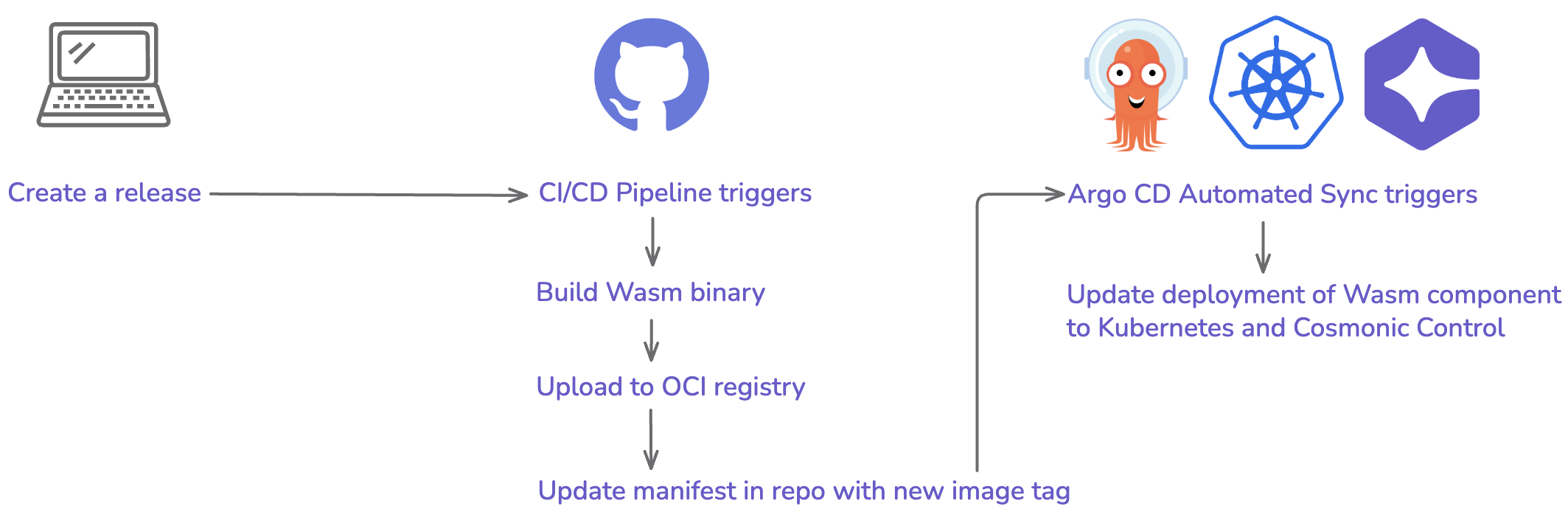
Once everything is set up, our GitOps process will look as follows:
- We create a release for a Wasm component in GitHub
- The release triggers a GitHub Workflow
- The Workflow run builds our Wasm component, uploads it to our GHCR registry, and submits a PR to update the image tag for our component deployment
- The manifest update triggers an automatic sync via Argo CD, which updates the deployed Wasm workload to the latest version
Deploy the hello-world Argo Application CRD manifest
To start, modify hello-proj.yaml to update the repoURL on Line 9 to target your new fork of the control-demos repo:
+ repoURL: https://github.com/<your-github-namespace>/control-demos.git
- repoURL: https://github.com/cosmonic-labs/control-demos.gitThe Argo Application is now targeting a manifest file in the hello-world directory of your control-demos fork.
Let's take a look at the HTTPTrigger CRD manifest serving as our deployment's source of truth:
apiVersion: control.cosmonic.io/v1alpha1
kind: HTTPTrigger
metadata:
name: hello-world
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 1
ingress:
host: 'hello.localhost.cosmonic.sh'
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
template:
spec:
components:
- name: http
image: ghcr.io/cosmonic-labs/control-demos/hello-world:0.1.2Don't make any changes at this stage, but note the OCI artifact we're using on Line 17: it's in the cosmonic-labs namespace and tagged 0.1.2.
Now apply the hello-proj.yaml Argo Application CRD manifest from integrations/argo-cd/:
kubectl apply -f hello-proj.yamlYou should quickly see the hello-world Application healthy and synced in the Argo CD dashboard.
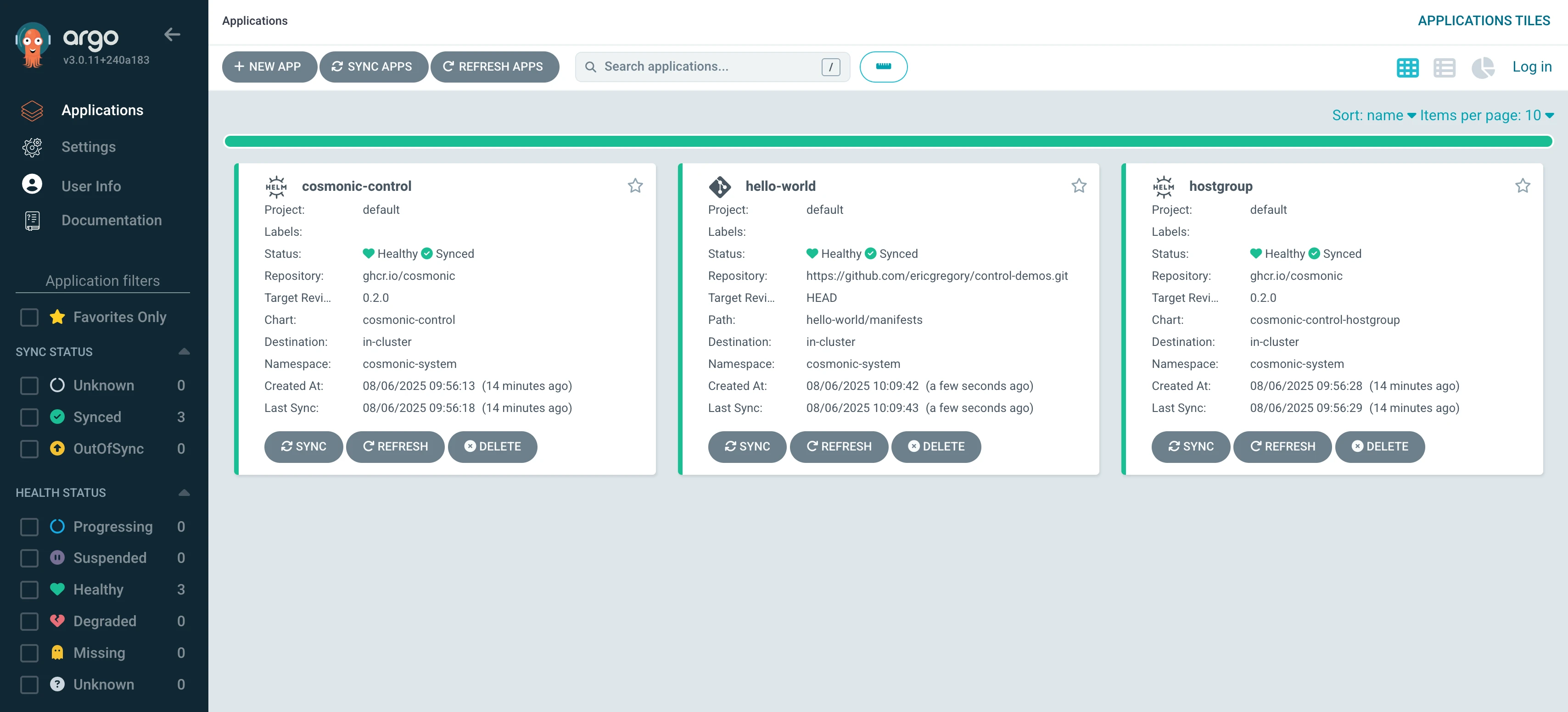
The hello-world Application is configured to Auto-Sync—when Argo detects changes to the source manifest, it will roll out an update to the deployment.
Optional: Modify the Wasm component
While not strictly necessary for the purposes of this example, at this stage you could use the GitHub web UI to edit the Rust code in hello-world/src/lib.rs and change the "Hello world" message, like so:
+ Ok(http::Response::new("Hello from Cosmonic Control and Argo CD!\n"))
- Ok(http::Response::new("Hello from Cosmonic Control!\n"))If you decide to edit the message, commit the changes.
Create a release
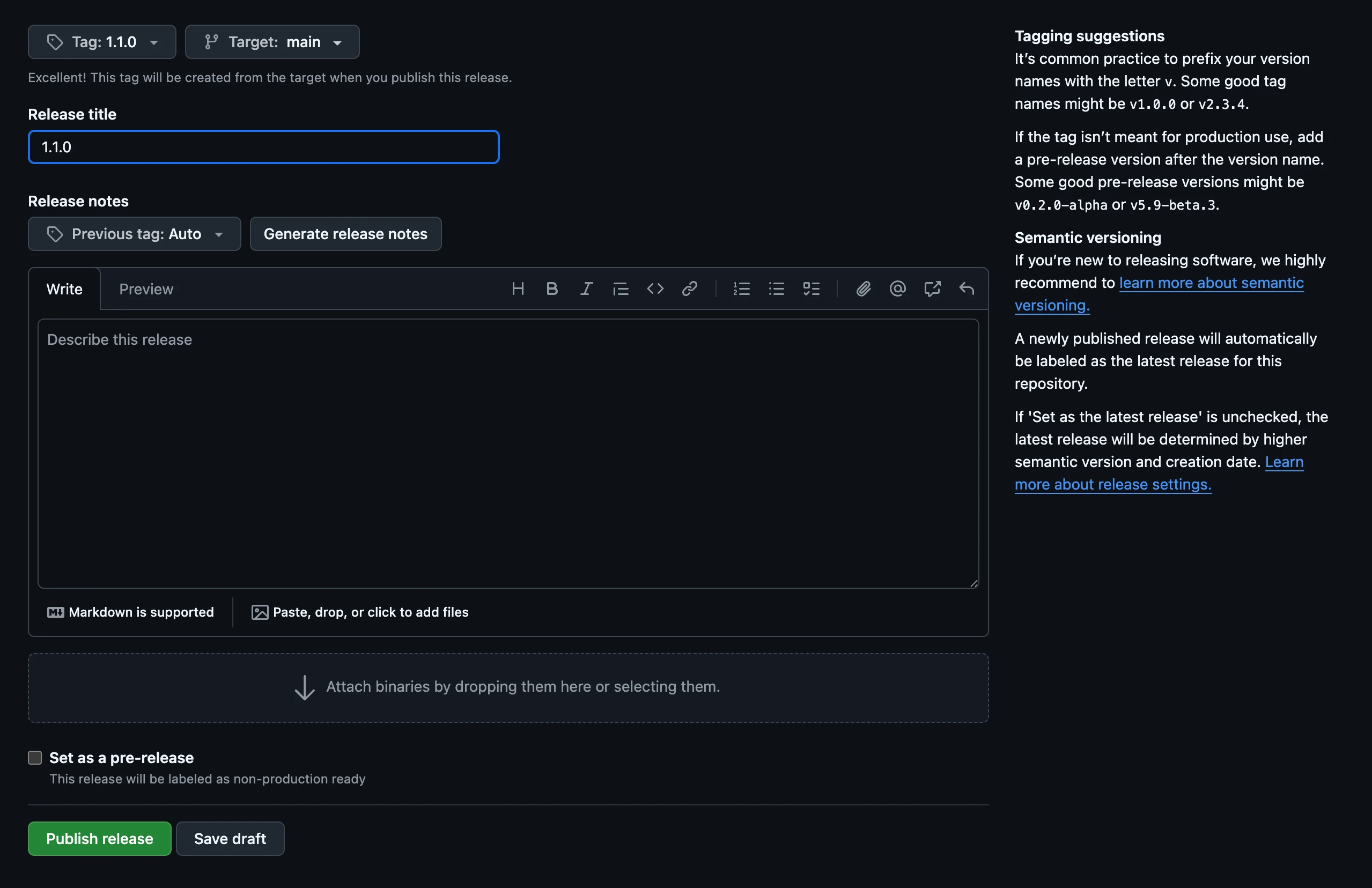
Now we'll create a release in GitHub. Click "Create a new release" in the right sidebar of your control-demo fork's repository page, or navigate to https://github.com/<your-github-namespace>/control-demos/releases/new.
Let's call our release 1.1.0. Create a new image tag, title the release, and click "Publish release."
Publishing the release will trigger a GitHub Workflow. (If you'd like to watch the run, you can click the "Actions" tab for the repo and select "publish" under Jobs.) This workflow will:
- Compile a Wasm binary from the Rust code in the hello-world directory using the setup-wash GitHub Action
- Push the Wasm component to ghcr.io as an OCI artifact under your namespace
- Update the image tag in the component's Kubernetes manifest to reflect the version of your new release
- Commit and push the manifest update in your repo
Note: The first time this workflow runs in your repository, it will take several minutes to build the necessary tooling, but those tools will be cached—future runs in the repo will generally take under a minute.
In the meantime, let's take a look at the last steps of the GitHub Workflow file:
- name: Update image tag in Kubernetes manifest
working-directory: ./hello-world
run: |
DEPLOYMENT_FILE="manifests/component.yaml"
OLD_IMAGE=$(grep "image:" "$DEPLOYMENT_FILE" | awk '{print $2}')
NEW_IMAGE="ghcr.io/${{ env.GHCR_REPO_NAMESPACE }}/components/hello-world:${{ github.ref_name }}"
# Update the image tag
sed -i "s|image:.*|image: $NEW_IMAGE|" "$DEPLOYMENT_FILE"
- name: Create Pull Request
uses: peter-evans/create-pull-request@v7
with:
token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
commit-message: |
Update image tag in manifest to ${{ github.ref_name }}
title: Update image tag in manifest to ${{ github.ref_name }}After building the component from your repo, the run submits a pull request updating the image specification in the hello-world manifest that our Argo CD hello-world Application is targeting, so that the manifest specifies a 1.1.0 image in your GHCR registry. This change to the manifest will trigger a sync in Argo CD.
Once the run completes successfully, merge the automated pull request, switch over to the Argo CD dashboard, and take a look at the hello-world Application. You should see that it has synced.
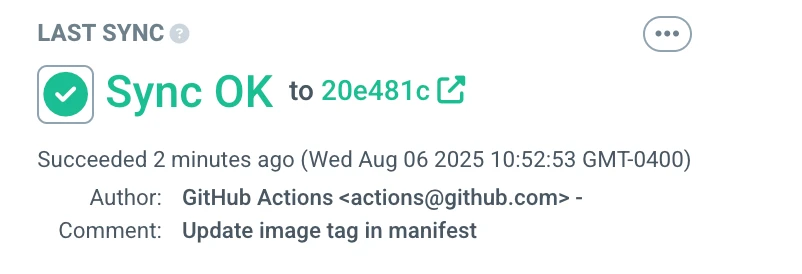
You can click through to see the commit that triggered the sync, or click on the Application at the left-hand side of the diagram and see the events associated with it:
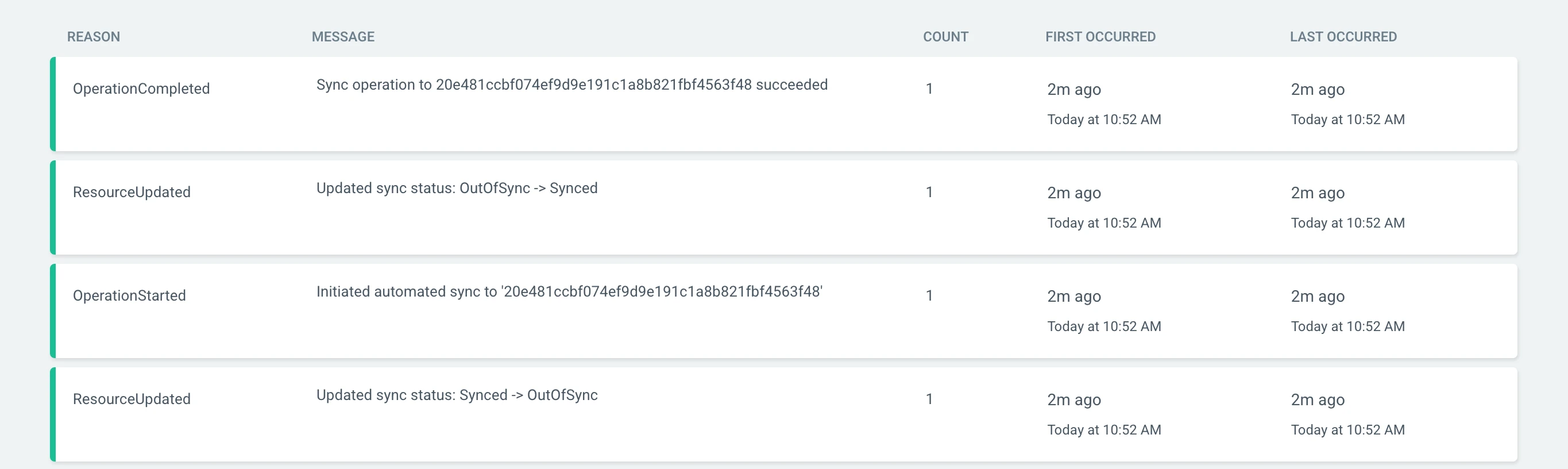
Test the deployment
In a new terminal tab:
curl http://hello.localhost.cosmonic.shHello from Cosmonic Control and Argo CD!Clean up
Once you're done, clean up your environment:
kubectl delete -f control-proj.yamlkubectl delete -f hostgroup-proj.yamlkubectl delete -f hello-proj.yamlhelm uninstall argocd -n argocdkind delete cluster